![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Previous
Next Top
Detailed TOC
Previous
Next Top
Detailed TOC
then replace the screen saver file (e.g. %SYSTEMROOT%\SYSTEM32\logon.scr if the 'logon' screen saver is active) with cmd.exe. When the screensaver starts, the command prompt will start instead (running in the SYSTEM context)!
The following is just to disable Guest on the older NT
3.51 and sync time.
net user Guest /active:no /passwordreq:yes
net time /domain /set
In the following, commands are listed which are suggested in the preceding sections for installing a server, they should not be regarded as complete, rather they are a starting point. Do not execute this script on your system unless you understand what it does!
net accounts /forcelogoff:30 /minpwlen:6 /maxpwage:90 /minpwage:3 /uniquepw:5 /domain
net accounts /sync
net user Guest /active:no /passwordreq:yes
net time /domain /set
diskperf -Y
cd \winnt35\system32
cacls \winnt35\system32\usrmgr.exe /E /R Everyone
cacls \winnt35\system32\regedt32.exe /E /R Everyone
The regedt32.exe utility allows direct editing of registry entries. While this can be very practical for changing parameters, but can render the system completely unusable!
The resource kit offers numerous (recommended) tools and lots of useful documentation (in paper and in the form of help files). The following are particularly useful:
| regentry.hlp | Documents registry entries. |
| nt35xkb.hlp | Knowledgebase articles on NT 3.5. Useful for troubleshooting. |
| winntmsg | The messages database |
| regini.exe | Set registry values from the command line. Very difficult to use and badly documented. Try the examples on the 3.51 resource kit CD in \support\suptools\i386\fifo*.ini. For NT4, use reg.exe |
| regback.exe | Backup registry hives to files. |
| regrest.exe | Restore Registry. |
| winat.exe | AT Scheduler graphical interface. See also soon.exe. |
| instsrv.exe | Install a service from the command line |
| rcmd.exe | Execute commands on a remote machine. See also remote.exe. |
| GUI utilities | dommon.exe, browmon, ntuucode and on NT4: wntipcfg.exe, clipstor, defptr and powertools are all worth a look. |
| POSIX utilities | This set of UNIX-like functions is particularly useful for administrators who manage a heterogeneous environment. The command set is quite limited: ls, cat, chmod, chown, cp, find, grep, ln, mv, touch, wc, vi. Many of the utilities work slowly and are badly integrated in the NT environment. I recommend the GNU win32 utilities with vim as a vi replacement, or those available in the "MKS Toolkit". The POSIX utilities from the 3.5 resource kit do not work with NT 3.51. |
| perl.exe | Perl 5 scripting language. Write all your scripts in perl! |
| c2config.exe | Utility which shows how well the machine conforms to C2 security and allows correction of certain security problems. See also following section. |
| srvcheck.exe | Command line auditing tool that shows what shares are exported with what permissions on a local or remote server. Error messages are obscure though. |
| srvinfo.exe | Command line auditing tool that shows what services are running, disks, CPU, network card/protocols/configuration, OS version, on a local or remote server. |
| dumpel.exe | Command line utility to dump event logs. e.g. dumpel -l security -s mycomputer |
| fixacls.exe | GUI to reset the NTFS permissions of system files to their recommended settings. |
| ntrights.exe | Command line tool to set/reset rights for users or groups of users. |
| findgrp.exe | Command line utility to show what groups a user belongs to.
e.g.: C:\util>findgrp localmachine mydomain\administrator The user is in the following MYDOMAIN Global Groups: Domain Users Domain Admins The user is in the following MYDOMAIN Local Groups: Users Administrators |
| getmac.exe | Command line utility to show MAC (Ethernet physical address).
e.g. C:\util>getmac Transport Address Transport Name ----------------- -------------- 00-80-5F-8C-72-AC \Device\NetBT_AMDPCN1 robocopy.exe useful for copying of lots of files from the command line. browstat.exe Command line for browser management. drivers.exe List drivers linked into the kernel, with memory usage. |
| pmon.exe | Command line process list (similar to the UNIX ps command). |
| pstat.exe | Similar to pmon, with details on events and handles. |
| diruse.exe | Examine size of directories |
| scopy.exe | Copy files & directories, maintain security settings. |
| netwatch.exe | Net Watcher shows which users are connected to shared directories and allows disconnection of users and un-share directories. It can simultaneously monitor multiple computers. |
The c2config.exe delivered with the resource kit, allows quick and easy auditing of C2 level security. It's use is highly recommended. When started on a new 3.51 server, the following screen is presented:
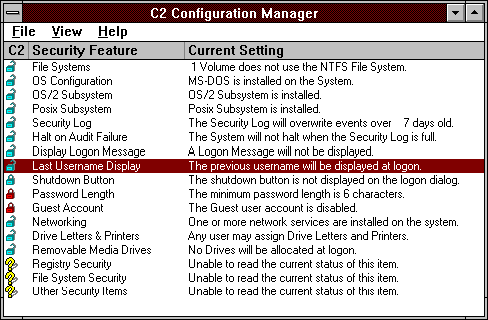
Above, only the password length and guest account conform to C2
security. It is recommended to secure the features as follows:
| Security Feature | Recommendation | Correctable with c2config.exe ? |
| File Systems | Secure, use NTFS when possible. | NT4, yes. 3.51, No. Use disk administrator. |
| OS Configuration | Secure. Where possible, DOS should not be installed. | No. Control Panel-> System-> timeout=0. |
| OS/2 Subsystem | Secure, disable OS/2. | Yes |
| POSIX Subsystem | No change. POSIX is useful for administration and does not pose significant risks. | ------ |
| Security | Secure, do not overwrite logs. | Yes |
| Halt on audit failure | No change if availability is very important. Secure if security is more important than availability. | Yes (not recommended) |
| Display Logon Message | Secure. Display logon message. e.g. Caption "My Company PLC", Message Text "Unauthorised access is prohibited and may be subject to prosecution." | Yes |
| Last Username Display | Secure. Hide last username logged in. | Yes. |
| Shutdown button | Secure. Don't show button in logon dialog box. | Yes. |
| Password Length | Secure. Passwords should have minimum length of 6 characters. | Yes |
| Guest Account | Secure. Where possible, disable the Guest account. | Yes |
| Networking | Keep. It is impossible to have no networking software installed! | No. |
| Drive letters & printers | Secure for sensitive systems. Only administrators should be able to assign drive letters and printers. | Yes. |
| Removable media drives. | Secure floppy. Allocate floppy drives at logon. CD-ROM drives are read-only, so there is no need to allocate at logon. | Yes. |
| Registry security | Secure. This enables you to assign Access Control Lists for the keys in the registry that restrict access to the system registry keys. The permissions applied are defined in the file c2regacl.inf. |
Yes. |
| File System Security | Secure. This enables one to assign Access Control Lists for the files in the system directories. The permissions applied are defined in the file c2ntfacl.inf. This file is in text readable format and can be extended to secure data or application directories. This will work fine if user directories & data are kept on a separate disk to the OS. Recommended as a general method for setting the system file permissions. |
Yes. |
| Other Security Items | C2config is not able to detect nor set all aspects of a Windows NT
system in order to make it conform to C2 Level Security. The following should be secured
manually:
|
No. How:
|
After securing as detailed above, the screen now shows:

This highly recommended FREE utility is very useful for examining filesystem permissions, file & printer shares, registry permissions, user & groups accounts and system policies, trusts, null sessions shares, rights and services. It has a GUI and command line interface and downloaded from www.systemtools.com/somarsoft .
The following analysis is based on V2.56, tested and used 1995, recent versions are very similar.
set TARGET=server1
echo Target computer = %TARGET%, writing results in subdirectory %TARGET%.mkdir %TARGET%
Echo Will now dump printers, shares, users, groups and policies...
pauseEcho Printers, shares, services and policies...
dumpacl /showaudit /rpt=printers /saveas=fixed /computer=%TARGET% /outfile=%TARGET%/printers.txt
dumpacl /showaudit /rpt=shares /saveas=fixed /computer=%TARGET% /outfile=%TARGET%/shares.txt
dumpacl /showaudit /rpt=services /saveas=fixed /computer=%TARGET% /outfile=%TARGET%/services.txt
dumpacl /showaudit /rpt=policy /saveas=fixed /computer=%TARGET% /outfile=%TARGET%/policy.txtEcho Users and groups ...
dumpacl /showaudit /rpt=groups /saveas=fixed /computer=%TARGET% /outfile=%TARGET%/groups.txt
dumpacl /showaudit /rpt=users /saveas=fixed /computer=%TARGET% /outfile=%TARGET%/users.txtEcho Files...
dumpacl /showaudit /rpt=dir=C:\ /saveas=fixed /computer=%TARGET% /outfile=%TARGET%/files_c.txt
Echo Registry HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE...
dumpacl /showaudit /rpt=registry=HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE /saveas=fixed /computer=%TARGET% /outfile=%TARGET%/HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE.txt
Echo Registry HKEY_USERS...
dumpacl /showaudit /rpt=registry=HKEY_USERS /saveas=fixed /computer=%TARGET% /outfile=%TARGET%/HKEY_USERS.txtNote: To see what lines are should really be where, set you browser to full screen
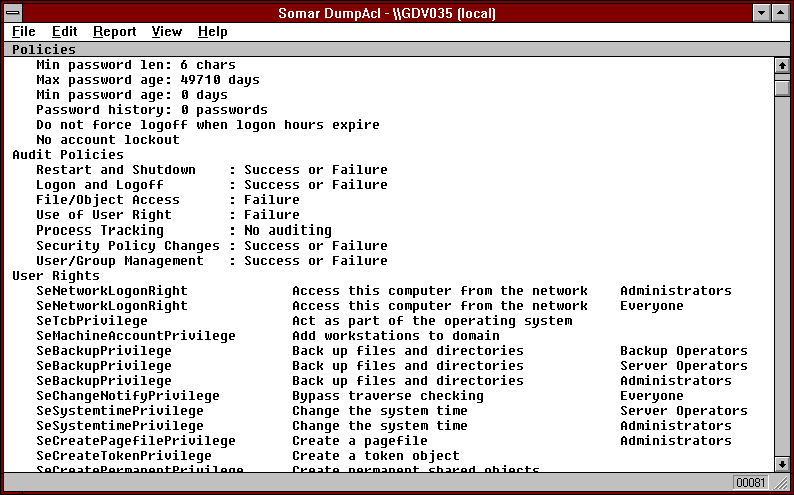
DumpAcl also has an interactive graphical interface. The reports may be viewed, printed or saved in a file. Recommended for system audits. The following is an example output of the policies report:
This cheap little tool (see www.soft4you.com or www.webdon.com ) takes snapshots of the registry & system files. It can also compare snapshots to show what keys or files have changed or been added/deleted. Interface is easy, output is either HTML or text.
From it's website:
"RegSnap is a tool that can help you analyze changes made to the Windows
Registry. With it, you can compare saved snapshots and learn which keys were
modified, deleted, or added. You can also analyze other sensitive system parts,
such as a list of files in Windows and Windows System directories, win.ini and
system.ini files, and autoexec.bat and config.sys files. RegSnap is able to
generate HTML reports, .REG files to undo and redo registry changes. Pro version
supports command line interface, Remote registry connection and OLE Automation
(i.e. could be scriptable from your programs)"
Tested V2.51 on NT4 SP3 in Dec.1998.
The standard command language of NT (like DOS commands) is
very limited.
The Perl 5 language is delivered with the NT resource kit. Perl is already
established and accepted as quasi standard in the UNIX system administration world. NT
Perl has evolved very fast and specialised modules are available on CPAN for user
administration, schedules, network administration, Web/Cgi etc.
The perl delivered with the resource kit tends to be out of date, update with a newer one from www.perl.com
Postmail.exe is a SMTP command line email client, which is very handy for mailing the output of programs/scripts to the system administrator (via UNIX email). It is freely available from www.software.com .
Footnotes:
[1] See [nt1] page 80-81.
[2] See [nt1] page 83.
[3] NT resource kit.
[4] See [nt2] Chap.3, customising setup.
[5] The Everyone & Administrator groups have the
right `Access from a Network'.
[6] Account operators cannot modify accounts of
Administrators, Domain Admins global group or the local groups: Administrators, Servers,
Account Operators, Print Operators, Backup Operators.
[7] Only if a user has the log on locally right, or access
to the User Manager for Domains program.
[8] See [nt6] page 87.
[9] See [nt1] page 110.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Previous Next Top Detailed
TOC IT Security Cookbook,
10 mars, 2002
Previous Next Top Detailed
TOC IT Security Cookbook,
10 mars, 2002